This post contains affiliate links. That means I may earn a small comision if you click on a link and purchase something. This cost you nothing. Read all the legal boring stuff here..
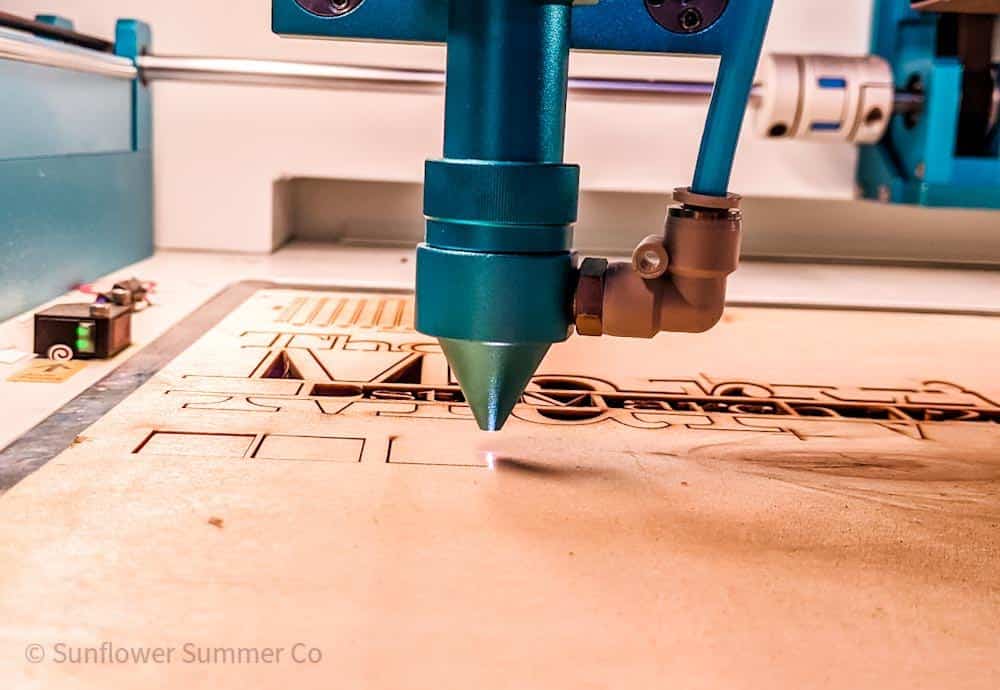
Laser cutting is a popular method for creating precise cuts in a variety of materials. One of the benefits of laser cutting is that the kerf, or width of the cut, is very small. In fact, the kerf from a laser cutter can be as much as ten times smaller than the kerf from a conventional cutting method such as sawing or milling.
While the kerf is generally not an issue, there are times when it can be problematic. Particularly when fitting laser-cut pieces together.
In order to avoid problems, it’s important to understand how laser kerf works and how to account for it when necessary.
What is Laser Kerf?
Laser kerf is the material that is burned away by the laser beam in order to create the cut line. The amount of material removed by the laser machine is very small, typically just a few hundredths of an inch.
This is much smaller than what you would get with any other type of cutting method.
A table saw has a kerf around 1/8″ or about the width of the saw blade.
Why is laser kerf important?
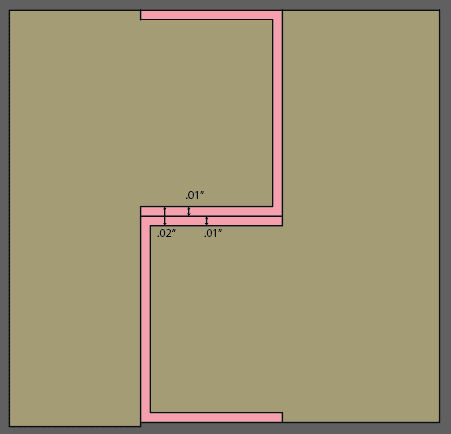
The laser kerf is important because when you are fitting laser cut pieces together like box joints(the typical joint in a laser project) you want the edges of the joints to rub against each other causing friction and pressure to keep the box together.
If the laser cuts off .01″ on each side of the joint, the joints are now .02 inches apart and will not hold together.
The pink line is what the laser cut out.
How Wide is Laser Kerf?
Laser kerf width can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of laser being used, the material being cut, and the thickness of the material.
In general, you can expect the kerf width to be between 0.004″ and 0.02″ depending on what material is being cut.
This is much smaller than what you would get with any other type of cutting method.
What is Kerf Allowance?
Kerf allowance is the amount of material that is allowed for the laser to burn away during the cutting process.
For example, if you are cutting something you want 1″ wide and your laser has a kerf of .01″, you would need to account for the kerf by making the piece you are cutting slightly wider.
In this case, you would cut the piece with a kerf of .01″ so the finished cut is 1″ wide.
Calculating and Finding the Laser Kerf
Finding the laser kerf is quite easy.
You will need a set of calipers and a 1″ laser-cut square from your machine.
The square should be cut from the same material you will be using for your project.
You will also want to have the same cut settings because different settings can create different kerf values.
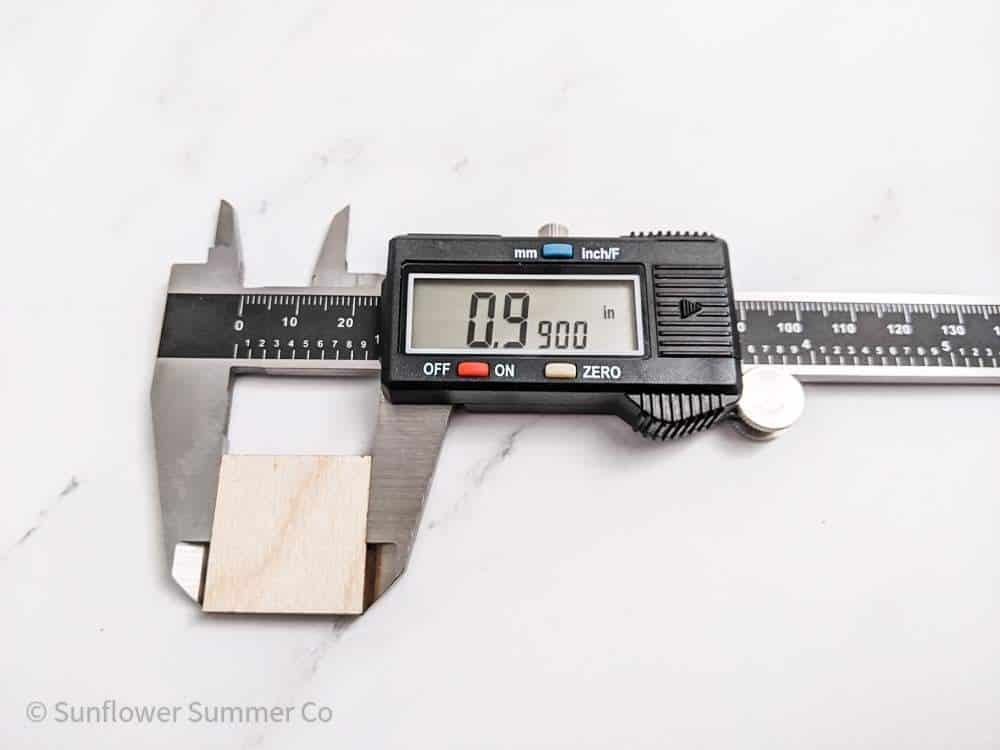
To find the kerf, simply cut out a square that is 1 inch across and measure it after your laser cuts it.
The difference between the size of the square on the computer and the actual size of the square divided by 2 will be the kerf.
For example, if the square measures .990 inches after being cut, then the kerf would be 0.005 inches.
As you can see, this one-inch square I cut out with my machine did not measure exactly 1 inch across.

You can follow this process for any new material you need to cut.
Every machine will also have a slightly different kerf. My Glowforge has a larger kerf than my Thunder Laser.
You will need to get a good pair of calipers for measuring the actual kerf amount.
I really like these ones.
Be sure to get metal calipers because they are much less likely to break. My plastic ones did not last very long but my metal ones are holding out strong.
When Kerf Can Be a Problem
Most of the time, the laser kerf will not have a significant effect on your project. However, there are times when it can be an issue.
Kerf can be a problem when fitting multiple pieces together like if you are making a box.
If you do not account for the kerf and you are using box joints, you will need to use glue to keep the box together.
If the fit is too tight, the pieces may not go together at all or they may be very difficult to put together.
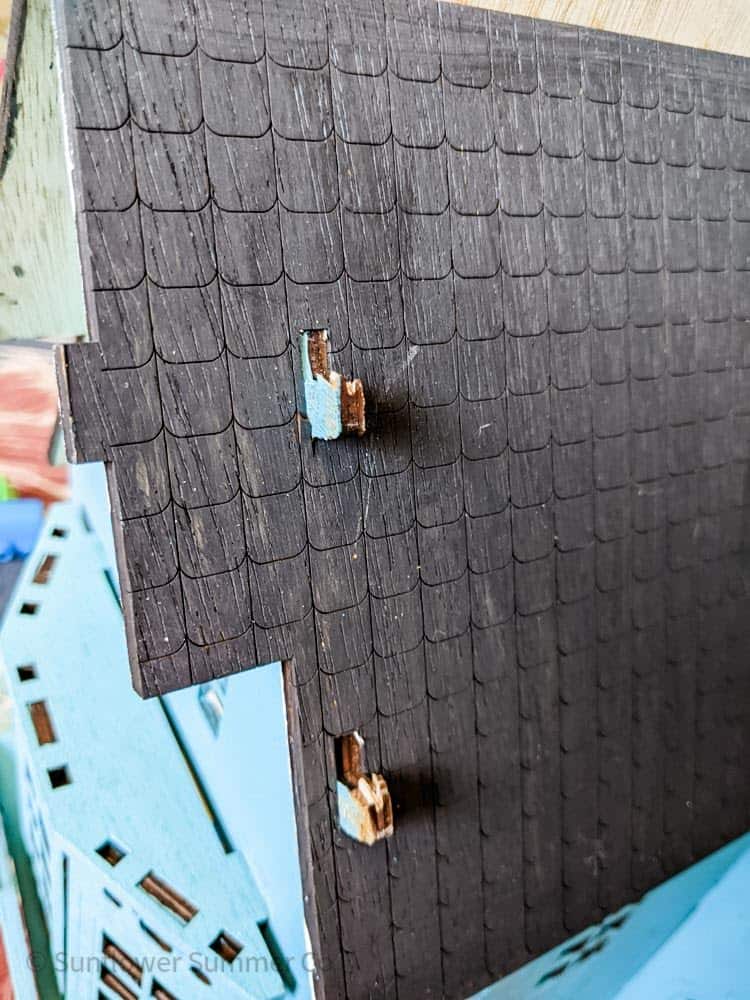
When building this doll house, I made the kerf offset too large and the pieces broke when putting it together.

How to Adjust for Kerf
The best way to start to account for kerf is to start by offsetting your shapes by half the width of the kerf.
Offsetting a shape is when you create a line around your design that is the same distance from the line all the way around.
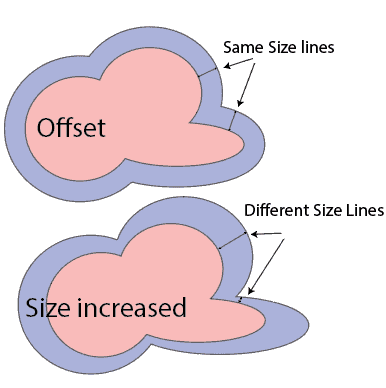
If you increase the size of the shape, the distance will not be the same all the way around messing up your cut.
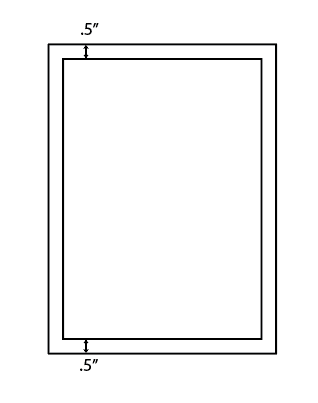
So, if you are using a 0.01 inch kerf, you would want to use the offset tool to offset your shapes by 0.005. This will ensure that the pieces fit together snugly without being too tight.
You want to divide the number in half because when you use offset, it offsets both sides and not just one.
So in this example, the offset is .5″ but it adds .5″ to both sides making it a total increase of 1″.
Keep in mind that the kerf can vary depending on the material you are using and the thickness of the material. So, it’s always a good idea to measure and account for the kerf before cutting your final piece.
What programs can I use to compensate for kerf?
There are a few programs that you can use to account for kerf. The first is a free program called Inkscape.
Check out this tutorial on how to offset in Inkscape.
You can also use Adobe Illustrator to offset your shapes to account for the Kerf.
Another program is LightBurn.
LightBurn is a program specifically for laser cutting and it has a feature that allows you to add an offset to your shapes without modifying the original design. You also do not need to divide the kerf in half.
Put in your kerf in the cut settings editor to quickly account for the kerf of any shape cut with these settings.
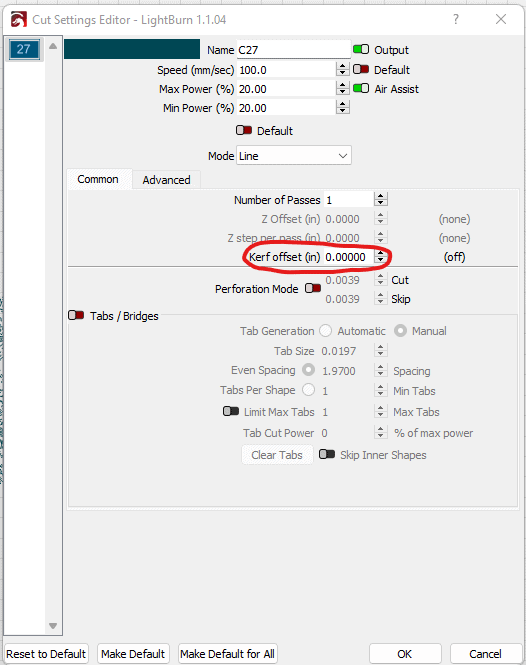
You can even save these settings to your library so you don’t have to remember your laser’s kerf for each material.
What can change laser kerf?
Material thickness, material type, cutting power, the wattage of the laser, speed of the cut, the focal length of the lens, and the type of laser head used can all change the kerf value.
Conclusion
With a little bit of understanding and adjustment, you can ensure that your laser-cut projects fit together perfectly.
By taking the kerf width of your laser cutter and adjusting your designs accordingly, you can avoid frustrating misfits and have beautifully cohesive pieces.





